Lava can be used to do functional tests on real hardware. It can be easily installed on PureOS, an FSDG compliant GNU/Linux distribution.
Labgrid has features similar to Lava but it is probably easier to learn because it's probably way easier to get started with it.
The OsmoGSMTester project is able to be interfaced with the Android RIL through ofono and can emulate a GSM network with the help of a compatible GSM base station or SDR.
This presentation from 2019 has many insights on what kind of issue we might expect in interfacing it with smartphones.
The Simtrace 2 project can be used, along with SIM card readers to programmatically feed a SIM card to a smartphone. This can be used to run test on real networks.
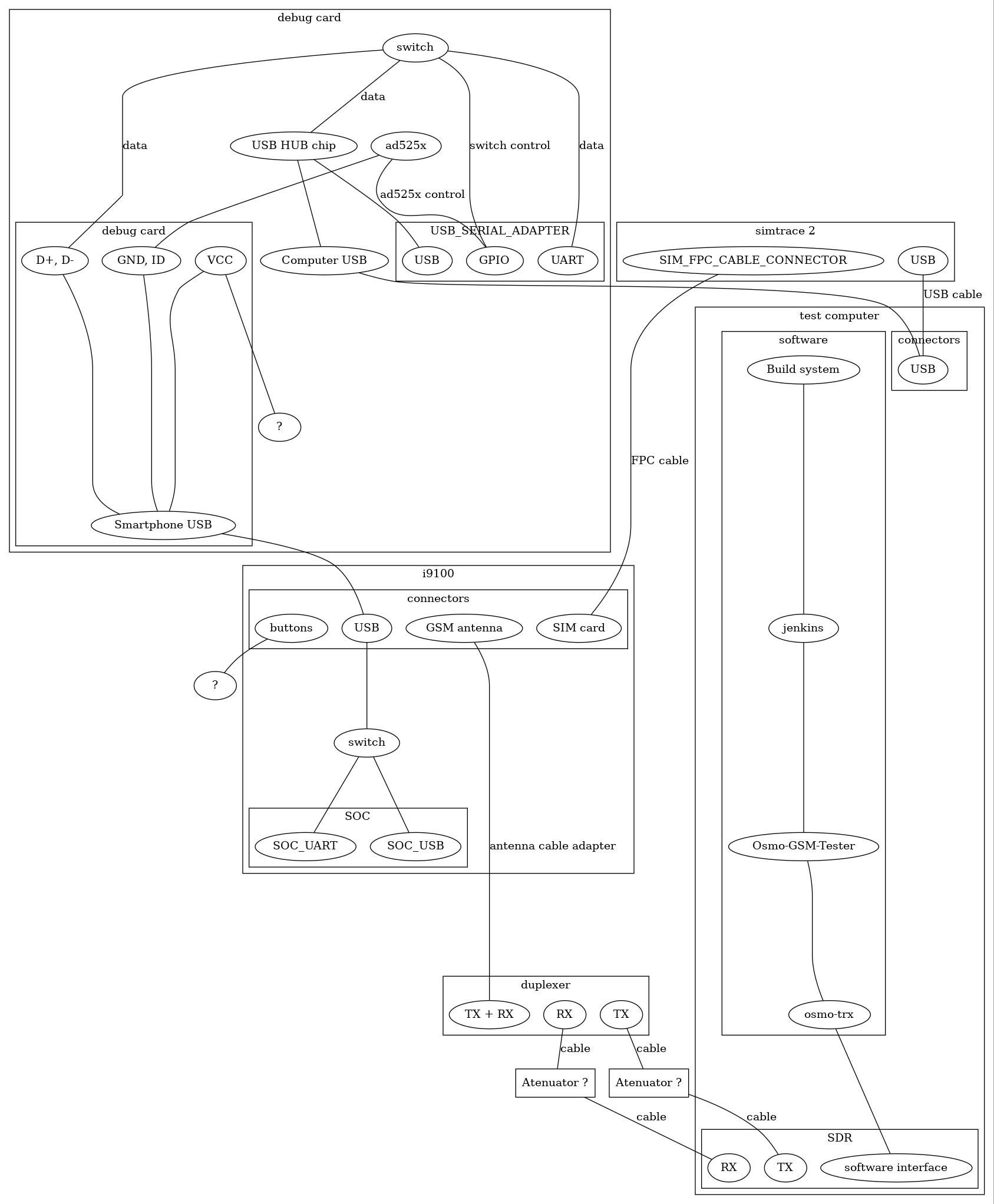
Serial port and USB:
Buttons:
Battery:
Antenna connector and GSM tower or SDR:See also the links inside the Serial_port article for more background on how to get serial port access on devices like the Galaxy SIII (GT-I9300) or the Galaxy SII (GT-I9100).

See https://git.replicant.us/contrib/GNUtoo/test-infrastructure.git for the source of the file.
| Device | Modem antenna connector | Compatible software | Comments |
| Motorolla C155 | MS-147 | * OsmocomBB * Old Nuttx revisions |
Could be used as reference phone as it's probably already supported by the Osmocom testing infrastructure |
| Galaxy SII (GT-I9100) | MS-162 | * Replicant 4.0, 4.2, 6.0 * Upstream Linux (partial) |
|
| Galaxy Nexus (GT-I9250) | ? | * Replicant 4.0, 4.2, 6.0 | We can get some GSM traces in wireshark with xgoldmon |
| Galaxy SIII (GT-I9300) | ? | * Replicant 4.0, 4.2, 6.0 * Upstream Linux (partial) |
When trying to enable protocol tracing in modems we can connect the device modem (somewhat directly) to a laptop
Questions:It might be possible to have a pure software test infrastructure with libsamsung-ipc.
It could be done more or less like that:
test script <-> ipc-modem or other programs <-> libsamsung-ipc <-> Linux kernel <-> VHCI <-> software sending USB packets
We have several choices for the Linux kernel:
| Kernels | Comments |
| User mode Linux (ARCH=um) | + Very lightweight, runs completely in userspace + Very simple setup. Probably works on armv7 too without dedicated hardware like Intel vt-x - Requires patches for USB / VHCI - Require dedicated RAM |
| Linux + libvirt + kvm | - Require some virtualization setup that requires dedicated RAM + Probably works unpatched |
| Project | Description | comments |
| gnuk | USB token software | can build for gnulinux |
| choptix | Library used by gnuk | More simple examples |
| CCID titan tests1[2] | CCID emulation | Probably uses vusb for testing too |
[1] https://git.osmocom.org/titan.TestPorts.USB/
[2]https://media.ccc.de/v/osmodevcon2019-128-osmo-ccid-firmware-libosmocore-talloc-on-uc-usb-testing-from-ttcn-3
So it might be possible to modify them to send some simple USB packets captured with wireshark / tshark / tcpdump.
| Settings | Status |
| kernel: kernel_replicant_linux commit: 843565d21f78 [WIP] ARM: dts: exynos: Add reboot modes to midas compilation settings: ARCH=um Host architecture: x86_64 kernel defconfig: x86_64_defconfig Target Distribution: Parabola x86_64 commandline arguments: ./linux mem=2047M ubd0=parabola.img root=/dev/ubda1 |
Boots fine |
| kernel: kernel_replicant_linux commit: 063228e445e2 net: sipc: core: fix code style compilation settings: ARCH=um Host architecture: i686 kernel defconfig: i386_defconfig |
Fails to compile1 |
| kernel: linux commit: f1baf68e1383 Merge tag 'net-5.17-rc4' of [...]kernel/git/netdev/net compilation settings: ARCH=um Host architecture: x86_64 kernel defconfig: i386_defconfig |
Boots fine |
| Target Distribution: Replicant 11 Build command: source build/envsetup.sh && lunch uml-userdebug && make dist kernel: ? kernel defconfig: ? |
Fails to compile2 |
1
CC arch/x86/um/user-offsets.s cc1: error: code model ‘large’ not supported in the 32 bit mode cc1: sorry, unimplemented: 64-bit mode not compiled in make[1]: *** [scripts/Makefile.build:117: arch/x86/um/user-offsets.s] Error 1 make: *** [arch/um/Makefile:118: archprepare] Error 2
2
[ 52% 179/339] including external/mesa3d/Android.mk ... FAILED: In file included from build/make/core/prebuilt.mk:53: In file included from external/mesa3d/Android.mk:124: In file included from external/mesa3d/src/mesa/Android.mk:23: external/mesa3d/src/mesa/Android.libmesa_glsl_utils.mk:74: error: BUILD_HOST_STATIC_LIBRARY is obsolete. Please convert to Soong. 12:25:14 ckati failed with: exit status 1 #### failed to build some targets (02:04 (mm:ss)) ####
To run Parabola first you need to create an image.
Then you need to chroot (with arch-chroot) insde the image and change the password.
Once you exited the chroot and unmounted the image and removed the loop mapping, you can boot it.
During boot you'll see a message like that at the end:
Virtual console 1 assigned device '/dev/pts/4'
You can then login in this way:
$ sudo picocom /dev/pts/4 picocom v3.1 port is : /dev/pts/4 flowcontrol : none baudrate is : 9600 parity is : none databits are : 8 stopbits are : 1 escape is : C-a local echo is : no noinit is : no noreset is : no hangup is : no nolock is : no send_cmd is : sz -vv receive_cmd is : rz -vv -E imap is : omap is : emap is : crcrlf,delbs, logfile is : none initstring : none exit_after is : not set exit is : no Type [C-a] [C-h] to see available commands Terminal ready parabola login: root Password: [root@parabola ~]# cat /etc/os-release NAME="Parabola" PRETTY_NAME="Parabola GNU/Linux-libre" ID=parabola ID_LIKE=arch BUILD_ID=rolling ANSI_COLOR="1;35" HOME_URL="https://www.parabola.nu/" DOCUMENTATION_URL="https://wiki.parabola.nu/" SUPPORT_URL="irc://chat.freenode.net#parabola" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://labs.parabola.nu/" LOGO=parabola [root@parabola ~]#